
The normal values were obtained if the number of correct answers was 88–100%.įor immittance audiometry (acoustic reflex and tympanometry), we used the Interacoustics 235 h clinical tympanometer through with a 226 Hz probe and the pressure measured in daPa. For the Speech Recognition Index, the list of monosyllabic words 40 dB above the mean tonal threshold of 0.5, 1, and 2 kHz was used for the test. The final result was the intensity when the participant obtained 50% of the words presented. For the speech Recognition Threshold, a list of disyllables was used. The assessment was performed in an acoustic booth using an Interacoustics AC40 audiometer with TDH39 headset calibrated in accordance with ISO-389 and IEC-645 norms. According to the classification of Davis and Silverman, the normal values of the auditory threshold were set down until 15 dB for air conduction and set down until 20 dB for bone conduction. Secondly, bone conduction thresholds were examined at 0.5, 1, 2, and 4 kHz. First, air conduction thresholds were tested at 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, and 8 kHz. The audiometric evaluation involved 2 types of thresholds. Thus, it possible to present a normative data for this equipment.

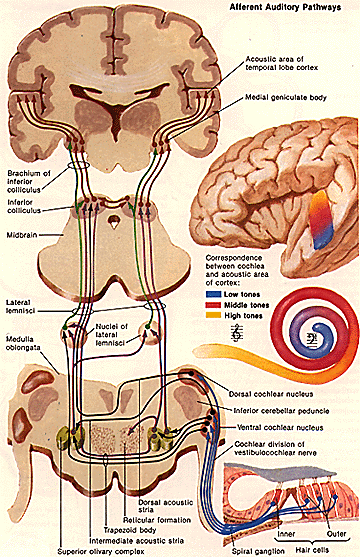
The objective of the present study is to latency values of wave I, III, V and interpeak intervals I–III, III–V, I–V values obtained in ABR evaluation using a newly equipment of ABR, the Neuro-Audio/ABR device by Neurosoft (Ivanovo, Russia). A new model of equipment for performing auditory evoked potentials has recently become available, the Neuro-Audio/ABR device by Neurosoft (Ivanovo, Russia). Equipment known and marketed for a long time has well-established normative standards.īut with new equipment, an important task is to provide normative data for that brand and model. The normative values of latency and interpeak intervals are based on population studies. Īccording to Esteves et al, different devices and examiners will yield distinct results thus, each institution should have its own standard set of parameters. Hearing deficits can be identified through analysis of these values. Assessments are made by measuring the absolute latencies of waves I, III, and V, together with the values of the interpeak intervals I–III, III–V, and I–V. Īssessment via ABR has been shown to be able to diagnose hearing disorders the technique plays a central role in the differential diagnosis of cochlear, retrocochlear, or conductive hearing loss. A variety of verbal and non-verbal stimuli can be used in the test, although a click is the best known and most used in clinical practice. The brainstem auditory evoked potential (ABR) is an important instrument for audiological diagnosis, allowing the integrity of the structures of the auditory system up to the brainstem to be tested.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
